Low Dielectric Resins (2): Features that are often used in product development in the electrical and electronic field !!
5G is now leading the way and 6G development is unstoppable~
In high-frequency and high-speed environments, low dielectric materials are gradually receiving attention!!
5G is the abbreviation of the fifth generation communication. Through the characteristics of high frequency and short wavelength, it can achieve faster and lower delay transmission effect, which is about 10 times higher than 4G transmission speed. In the technology era where 5G is prevalent, the connected value chain spans across telecommunications services, 5G network equipment, 5G infrastructure, 5G semiconductors, 5G consumer goods, etc. Frequency characteristics and the resulting high heat dissipation and low loss requirements have gradually attracted attention.

▲In the era of high-speed transmission, many new technological applications have been born
Low dielectric materials
In the application field of 5G, the characteristics that attract the most attention at present are the dielectric constant and dissipation factor of materials. The dielectric constant is a physical quantity that characterizes the response of a material to an electric field. The lower it is, the less susceptible it is to being affected by an electric field. Materials with lower dielectric properties can produce less loss under high-frequency transmission such as 5G, reduce signal loss, and reduce the pressure on heating conditions and heat dissipation functions. For example, in the PCB industry, copper foil substrate (Copper Clad Laminate, CCL), which accounts for nearly half of the cost, can be used in the development of low-dielectric materials, which is also one of the current hot topics. The corresponding upstream materials may include low-dielectric resin, low-dielectric glass fiber material, and low-dielectric filling material. The following table lists possible potential materials for resin, reinforcing materials, and filler materials in low dielectric applications based on the main components of the copper foil substrate.
| Application | Resins | Reinforcing materials | Fillers |
| FR-4 | Epoxy resin, phenolic resin, polyamine formaldehyde | Glass fiber cloth | Silicon dioxide |
| Low dielectric substrate | Polyphenylene ether, polytetrafluoroethylene, petroleum resin, low dielectric epoxy | Low dielectric glass fiber | Hollow silicon dioxide, hollow acrylic microspheres, hollow glass microspheres |
Dielectric constant and loss factor of various resins (thermoset, thermoplastic)
Since resin has many advantages, such as excellent chemical resistance, electrical insulation, adhesion, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, ease of processing, etc., it also plays an important role in electronic-related applications. The following table shows the dielectric constants and loss factors of various common resin types. The most common epoxy and phenolic resins have the highest dielectric constants among them. Polyphenylene ether and tetrafluoroethylene have lower dielectric constants and are emerging materials favored by the trend of high-frequency transmission.
| Resin | Dk (1 MHz) | Df (1 Mhz) |
| Phenolic resin | 3.1-4.0 | 0.03-0.037 |
| Epoxy resin | 3.0-3.9 | 0.01-0.03 |
| Cyanate resin | 2.7-3.2 | 0.004-0.010 |
| Silcone resin | 2.8-2.9 | 0.002-0.006 |
| Polymide (PI) | 2.7-3.2 | 0.005-0.008 |
| Bismaleimide (BMI) | 2.8-3.2 | 0.005-0.007 |
| Polyester resin | 2.7-3.2 | 0.005-0.020 |
| Hydrocarbon resin | 2.2-2.6 | 0.001-0.005 |
| Modified polyphenylene oxide (PPO)/ Polyphenylene ether (PPE) | 2.45 | 0.0007-0.001 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 2.8-3.8 | - |
| Cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) | 2.3 | 0.00007 |
| Poly(p-phenylene sulfide) (PPS) | 3.0 | 0.002 |
| Poly(ether sulfone) (PES) | 3.5 | 0.003 |
| Polysulfone (PSF) | 3.0-3.2 | - |
| Poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEK) | 3.2 | 0.003 |
| Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) | 3.4-3.5 | - |
| Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) | 2.9 | 0.002 |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 2.4-3.1* | 0.0002(1GHz)* |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 2.3-2.4* | - |
| Poly tetra fluoro ethylene (PTFE) | 2.1 | 0.0004 |
(Development of Halogen Free, Low Loss Copper-Clad Laminates Containing a Novel Phosphonate Oligomer, Y. Qiang, 2016)
*(https://www.professionalplastics.com/, Electrical Properties of Plastics)
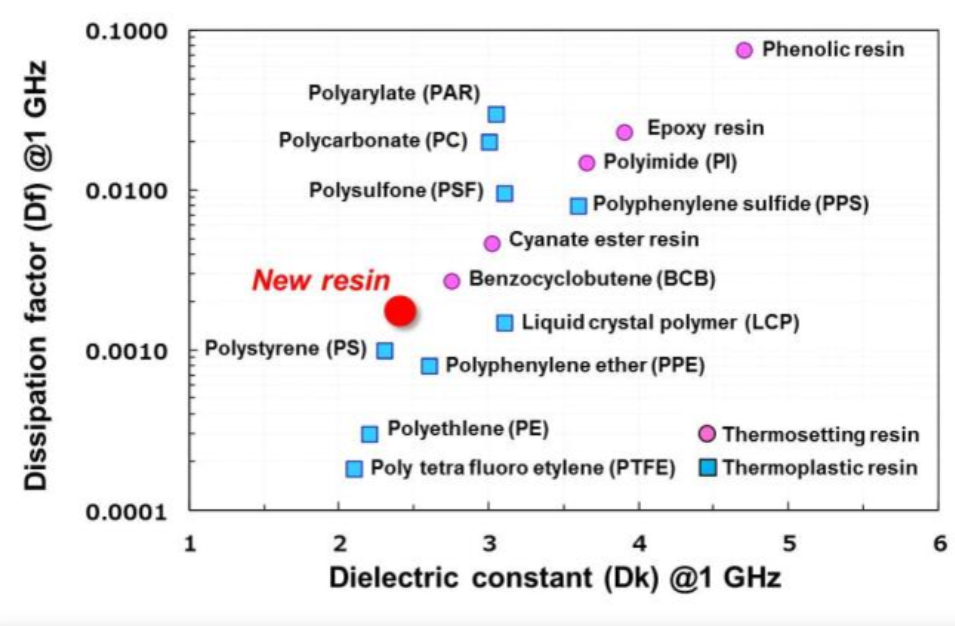
Comparsion of the dielectric constant (Dk) and loss factor (Df) between resins
If the resin is divided into thermosetting type and thermoplastic type, draw a graph according to its dielectric properties, as shown in the figure below. It can be found that common thermosetting resins, such as phenolic resins, polyimides, and epoxy resins, are all in the upper right of this figure in comparison, and their dielectric constants and dissipation factors are relatively high. Polycarbonate has a small dielectric constant but a high loss factor. However, polytetrafluoroethylene is a material with relatively low two values, so it has attracted special attention in the development of 5G low-dielectric materials. However, because the cost is still relatively expensive compared with other materials, it has not been widely used.
(Tanigawa, Takao et al. “Low Transmission Loss Film Material for High-Speed High-Frequency Devices.” 2018 IEEE 68th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC) (2018): 1757-1761.)
Low dielectric epoxy
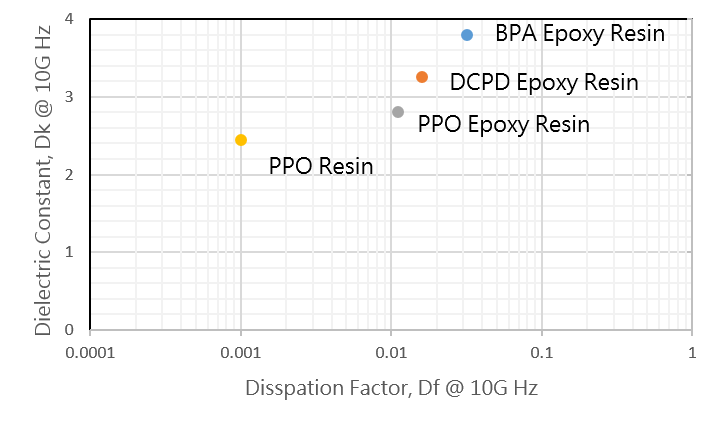
At present, low-dielectric epoxy resins have been developed on the market, which can provide excellent chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and low dielectric properties at the same time. The main difference between low-dielectric epoxy resin and ordinary epoxy resin is their dielectric constant, which can meet the same requirements in the application of materials. Therefore, low-dielectric epoxy resin has better signal transmission efficiency and anti-interference ability, and is suitable for high-speed, high-frequency, and high-density electronic products. The dielectric constant of low-dielectric epoxy resin is generally around 3, while that of ordinary epoxy resin is generally around 4. The following table shows the relevant numerical differences between general type and low dielectric epoxy resin.
| Item | General epoxy resin | Low dielectric epoxy | Low dielectric epoxy |
| Epoxy type | bisphenol A, BPA | Dicyclopentadiene, DCPD | polyphenylene oxide, PPO |
| Tg (oC) | 168 | 169 | 160 |
| Dk (10 GHz) | 3.8 | 3.25 | 2.8 |
| Df (10 GHz) | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.011 |
| CTE (ppm/o C)* | - | 54 | - |
*Hardener: Novolak, Catalyst: 2-Methylimidazole, Curing Condition: 170 oC dry 240 oC press
Plot the Dk/Df values of various types of epoxy resins as shown in the figure below. It can be found that through the improvement of epoxy resin, the dielectric properties are gradually approaching the low dielectric polyphenylene ether resin, and it has the characteristics of epoxy. Low dielectric epoxy has broad development prospects. It will play a greater role in high-end application fields such as high-speed transmission and wireless communications.
CONTACT US
Kelly Chemical Corporation
Electronics
TEL:(02)2762-1985 ext 11200
Online Message
Leave your contact information,
and we will get in touch with you soon.
Email Consultation
After receiving your email,
we will process it as soon as possible.send Email