Phenolic Epoxy Resin~Application introduction from floor paint to semiconductor molding materials!
According to different applications, select phenolic epoxy with distinctive characteristics.
From floor coatings, PCB inks, laminates to semiconductor mold sealing materials.
Epoxy resin is a compound with epoxy groups in its molecular structure, widely used in composite materials, castings, paints, inks, etc. The current common synthetic method involves the condensation reaction of epichlorohydrin and bisphenol A. Then, epoxy resin reacts with a curing agent to form a cross-linked structure, resulting in cured products with excellent chemical resistance and strength. Therefore, both the curing agent and the resin itself are of considerable importance. In recent years, due to the increasing focus on sustainability and low carbon issues, bio-based carbon epoxy resins have also appeared on the market. In addition to the additional value of biomass, they also maintain similar physical properties to conventional epoxy resins.
(Extended Reading:Bio epoxy resin, green, low-carbon, environmentally friendly materials that meet the trend!!)

▲The application of phenolic epoxy resin in floor coatings is already quite mature.
In addition to curing agents, epoxy resins are often used in combination with inorganic fillers to enhance the strength of the material and save resin usage. Common fillers include titanium dioxide, silica, alumina, ceramic powders, etc. Taking the application of sealing materials as an example, possible formulations, curing conditions, and related physical properties are as follows:
Molding Compound Application
|
Component |
Values |
|
|
Formulation (phr) |
Standard Solid Epoxy Resin |
100 |
|
DDM |
9.6 |
|
|
Calcium Stearate |
3 |
|
|
Silica |
250 |
|
|
Reaction conditions |
Blending (oC/min) |
25-57/5 |
|
Aging (min at 80oC) |
43 |
|
|
Physical properties |
H.D.T(oC) |
105.5 |
|
Barcol Hardness |
52 |
|
|
Water Absorption (1hr boiling, wt.%) |
0.212 |
|
|
Flexural Strength (KG/mm2) |
12.7 |
|
|
Volume Resistivity (ohm-cm) |
1.7x1014 |
|
*Molding Conditions: Pressure 100-200KG/CM2 x 10 MIN at 150°C
(Further Reading:Advantages and disadvantages of spherical Alumina(Al2O3) manufacturing method )
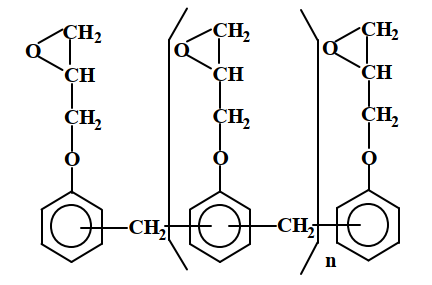
Phenolic epoxy resins, due to their excellent chemical resistance, heat resistance, and lower coefficient of thermal expansion, possess balanced physicochemical properties and economic feasibility. They are widely used in fields such as electronics and electrical engineering, for example, in electronic component materials, laminates, etc. Phenolic epoxy resins can further be divided into Phenol Novolac Epoxy (PNE) and Cresol Novolac Epoxy (CNE). Below are explanations for these two categories:
Phenol Novolac Epoxy (PNE)
Phenol Novolac Epoxy is synthesized by the reaction of epichlorohydrin with phenolic resin and exhibits good chemical resistance, stability, and strength. However, it has relatively poor flexibility and is prone to brittleness. If its advantages are utilized properly, it can be applied in structural adhesives, laminates, composite materials (yachts, pipelines, automotive components), PCB solder mask inks (PSR Ink), etc.
Common Specifications of Four Types of Phenol Novolac Epoxy Resins
| Category | Epoxy Equivalent(g/eq) | Viscosity(25oC) | Color(G) | Application/Characteristics |
| A | 160-180 | 9,500-12,500 | <1 |
High heat resistance, low viscosity |
| B | 165-185 | - | <3 |
heat resistance, low viscosity |
| C | 170-190 | - | <3 | High heat resistance |
| D | 165-185 |
10,000- 20,000 |
<3 |
High heat resistance, low viscosity、FDA 21 CFR |
▲Phenolic epoxy resin chemical structure
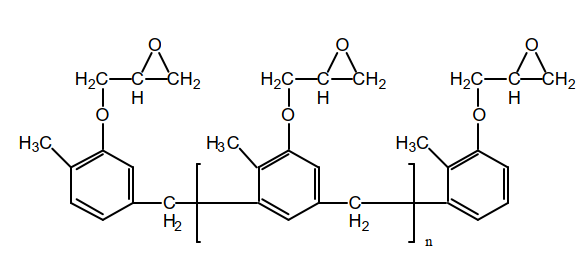
o-Cresol Novolac Epoxy, CNE
This type of resin exhibits high heat resistance and chemical resistance and is suitable for applications requiring high Tg and low CTE material properties. With multiple epoxy functional groups in one molecule, it undergoes complete cross-linking, resulting in excellent physical properties after curing. It can undergo curing reactions with curing agents such as polyamine, polyaminodiamide, carboxylic resins, phenolic resins, phenol novolac resins, and anhydrides. Applications include powder coatings, PCB inks, and other applications requiring heat resistance, chemical resistance, and waterproofing. Additionally, it has certain advantages in applications requiring good electrical properties such as molding compounds (EMC), laminates, and underfill. With advancements in semiconductor technology, materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion have become mainstream.
Common Specifications of Four Types of o-Cresol Novolac Epoxy Resins
| Category | Epoxy Equivalent(g/eq) | Softening Point (oC) | Hydrogen Chloride(ppm) | Color(G) | Application |
| A | 190-210 | 50-54 | <350 | <2 | EMC, laminates, coatings |
| B | 200-212 | 60-65 | <350 | <2 | EMC, laminates, coatings |
| C | 190-220 | 85-95 | <350 | <2 | EMC, laminates, coatings |
| D | 190-220 | 95-100 | <350 | <2 | EMC, laminates, coatings |
▲Chemical structure of o-cresol novolac epoxy resin
Epoxy Floorings/ Coatings
Epoxy resins, due to their unique chemical and mechanical properties, have extensive commercial possibilities, with their application in floor coatings having a long history. Epoxy resin's application in floor coatings is particularly advantageous due to its chemical resistance and strength, resulting in characteristics such as high abrasion resistance, durability, and decorative features. It is typically applied on concrete surfaces through multiple layers of resin coating or pouring, forming a strong and permanent protective layer after complete curing. The thickness of epoxy resin flooring and epoxy resin floor coatings typically differs, with flooring thickness usually ranging from 2-4mm and floor coating thickness typically ranging from 0.5-1mm.Epoxy Flooring Types:
- Self-leveling epoxy flooring: Smooth surface, mainly used in garages, sports facilities, kitchens, warehouses.
- Epoxy mortar flooring: Corrosion-resistant and impact-resistant, mainly used in factories, machinery, warehouses, garages.
- Quartz-filled epoxy flooring: Decorative appearance with anti-slip properties, mainly used in schools, exhibition halls, offices.
- Epoxy antistatic flooring: Eliminates potential discharges, mainly used in warehouses storing any flammable gases or liquids.
According to the Resin Flooring Association (FeRFA) guidelines for synthetic resin flooring, different types have different load-bearing capacities and thicknesses. Below are several common types of flooring:
| Type | Description | Load Bearing | Thickness |
| Floor Seal |
Applied in two or more layers, usually solvent or water-based |
Light | 150um |
| Floor Coating |
Applied in two or more layers, usually solvent-free |
Light/Heavy | 150-30um |
| High Build Paint Floor |
Applied in two or more layers, usually solvent-free |
Medium | 300-1,000um |
| Multi-layer Floor | Multi-layer coating or self-leveling floor laying | Medium/Heavy | >2 mm |
| Self-leveling Floor | Smooth surface | Medium/Heavy | >2-3 mm |
| Resin Mortar Floor | Usually includes surface seal coating to reduce pores | Medium/Heavy | >4 mm |
| Heavy-duty Self-leveling Floor | Smooth surface | Heavy/Extra Heavy | 4-6 mm |
| Heavy-duty Resin Floor | System with aggregate fill, ensuring overall impermeability | Extra Heavy | >6 mm |
(Source:FeRFA, Guide to the specification and application of synthetic resin flooring)
Paint Application Reference Formulation and Physical Properties
| Component | Values | ||
| Component Percentage Formulation(wt.%) | Phenol Novolac Epoxy Resin | 32 | |
| Titanium Dioxide | 18 | ||
| Talc | 20 | ||
| Thinner | 11 | ||
| Additives | 3 | ||
| Alicyclic amine curing agent | 16 | ||
| Reaction Conditions | Mixing A:B ratio(wt.%) | 84:16 | |
| Dye volume concentration(%) | 30 | ||
| Volume solids (%) | 65 | ||
| Curing Conditions | 25oC for 7 days | ||
| Physical Properties | Usage Time | 4 hr 30 min | |
| Drying Time | dry to touch | 2 hr | |
| Fully dry | 7 hr 30 m | ||
| Shore Hardness | 77 | ||
| Wear Resistance (mg/weight loss) | 61 | ||
| Chemical Resistanc (25oC for 14 days) | 50% NaOH | No foaming, softening, swelling, loss of adhesion | |
| Phenol | |||
| Tetrahydrofuran | |||
| Methanol | |||
PSR Ink/ Solder Mask
In printed circuit boards, solder masks or solder resist layers are usually applied to protect copper traces and prevent short circuits, protecting the circuits from oxidation or dust contamination. Phenolic epoxy resins are one of the most advantageous materials for solder masks due to their relatively low thermal expansion rates. Solder masks are typically divided into three major types:
- Epoxy Liquid Solder Mask:
This is the most economical method, using screen printing to cover the areas that need protection. Despite its long history of use, it remains the most cost-effective method for large-scale production of printed circuit boards.
- Liquid Photo Solder Mask (LPSM/Liquid Photo Imageable, LPI):
Usually formulated with epoxy resin and epoxy acrylate resin, suitable for situations where printed circuit boards are relatively uneven. It can be applied using screen printing or coating methods on the circuit board and is commonly used in both flexible and rigid circuit boards. Due to its high stability and precision, LPI can form a very tight contact with the circuit board, making it highly durable and currently the most commonly used solder mask technology.
- Dry Film Solder Mask (DFSM):
Comparatively more expensive than liquid photo imaging, dry film is vacuum-laminated onto the PCB and then exposed and developed. It is the most advantageous for flat PCBs, forming a uniform surface thickness.
Epoxy Molding Compound, EMC
Epoxy molding compounds are widely used in various packaging fields such as consumer electronics, ICs, automotive electronics, semiconductor components, etc. For example, in semiconductors, from traditional wire bonding to ball grid array packaging, these materials are used. Electronic packaging can protect internal components from external factors (such as moisture, dust), maintaining product stability and yield. As electronic products become smaller, packaging technology needs to perform more stable in a more limited space, making EMC more important in the packaging of micro-components. Typical molding compounds usually consist of epoxy resin, curing agent, additives, fillers, catalysts, etc., and are cured at high temperatures. Below are reference formulations and physical properties.
Reference Formulation and Physical Properties of Molding Compounds
| Component | Values | ||
| Formulation (wt.%) |
o-Cresol Novolac Epoxy Resin Silica Micro Powder Phenolic Resin TPP Toughening Agent Other Additives total |
16 70 8.5 0.3 2 3.2 100 |
|
| Physical Properties | Vortex flow length (inch) | 33.5 | |
| Gelation time(sec) | 26.9 | ||
| Resin exudation(mm) | 1.43 | ||
| Hardness | 88 | ||
| Bending Strength(Kgf/mm2) | 14.5 | ||
| Flexural Modulus (Kgf/mm2) | 1,388 | ||
| Purity | Cl- (ppm) | 4.5 | |
| Fe+ (ppm) | 2.2 | ||
| Na+(ppm) | 3.3 | ||
(Further Reading: Low chlorine epoxy resin (1): Characteristics commonly used in product development in the electronic and electrical fields!! )
Laminate
Phenolic epoxy resins, due to their excellent chemical resistance, heat resistance, wear resistance, and moisture resistance, are commonly used in the field of composite materials. Compared to polyurethane, they exhibit lighter and stronger performance, making them quite common in laminate applications. By combining epoxy resins with other materials through different combinations and designs, products with high strength and durability can be manufactured. Common products include boat decks, automotive components, electrical insulation components, etc.
Furthermore, epoxy laminates are extensively used in the PCB industry as the substrate for copper-clad laminates (CCL). Various types of substrates such as FR-3, FR-4, FR-5, CEM-1, CEM-2, CEM-3, CEM-4, and others utilize epoxy laminates as their material.

▲Phenolic Epoxy Resin with Good Chemical Resistance and Physical Properties
Application Reference Formulation and Physical Properties for Laminates
| Component | Ratio | |
| Formulation |
o-Cresol Novolac Epoxy Resin MEK DDS BF3MEA BDMA Thinner |
100 25 - 63.6 1.1 - |
| Reaction Conditions | B-Stage(oC/min) | 130/10 |
| Press(Kg/cm2/oC/min) | 15/170/120 | |
| Physical Properties | Barcol Hardness | 70 |
| Bending Strength(Kg/mm2) | 54.2 | |
| Tensile Strength(Kg/mm2) | 39.5 | |
| Volume Resistivity(ohm-cm) | 1.59x1016 | |
| Resin Content (%) | 36.7 | |
CONTACT US
Kelly Chemical Corporation
Electronics
TEL:(02)2762-1985 ext 11200
Online Message
Leave your contact information,
and we will get in touch with you soon.
Email Consultation
After receiving your email,
we will process it as soon as possible.send Email